EulerRKConvergenceDemo.m
Contents
Overview
This script illustrates the different convergence behavior of
- Euler's method (implemented in Euler.m),
- the classical second-order Runge-Kutta method (implemented in RK2.m),
- the classical fourth-order Runge-Kutta method (implemented in RK4.m)
for the problem

on the interval ![$[0,10]$](EulerRKConvergenceDemo_eq13266.png) with exact solution
with exact solution

Code
Set up the problem
clear all close all f = @(t,y) -y+2*exp(-t).*cos(2*t); t0=0; y0=0; % initial condition tmax = 10; Nvalues = [20 100 500];
Run for several different values of  , the number of steps used to reach the final time
, the number of steps used to reach the final time  .
.
for N=Nvalues
h=tmax/N;
[t1,y1] = Euler(t0,y0,f,h,N); % call Euler.m
[t2,y2] = RK2(t0,y0,f,h,N); % call RK2.m
[t3,y3] = RK4(t0,y0,f,h,N); % call RK4.m
figure
hold on
title(sprintf('Approximate solutions with %d points',N))
xlabel('t'), ylabel('y')
xlim([t0 tmax]), ylim([-0.2 1])
plot(t1,y1,'b',t1,y1,'ro','LineWidth',2);
plot(t2,y2,'m',t2,y2,'ro','LineWidth',2);
plot(t3,y3,'k',t3,y3,'ro','LineWidth',2);
legend('Euler solution','Euler points','RK2 solution','RK2 points',...
'RK4 solution','RK4 points',-1);
pause
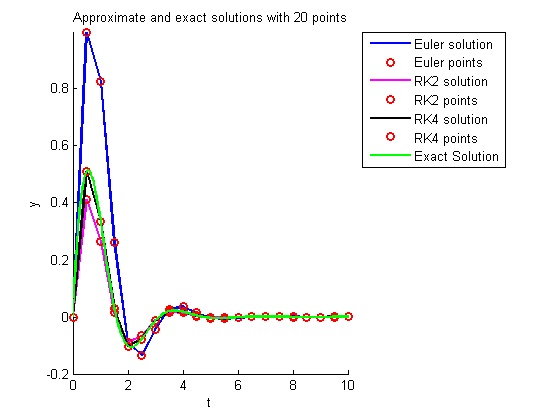
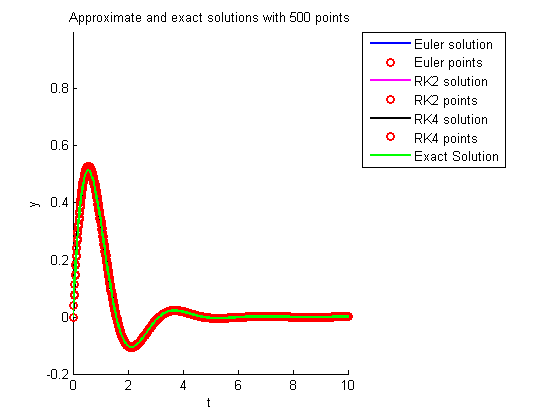
title(sprintf('Approximate and exact solutions with %d points',N))
tt=linspace(0,10,201);
plot(tt,exp(-tt).*sin(2*tt),'g','LineWidth',2); % exact solution
legend('Euler solution','Euler points','RK2 solution','RK2 points',...
'RK4 solution','RK4 points','Exact Solution',-1);
hold off
pause

Compute errors and approximate rates of convergence
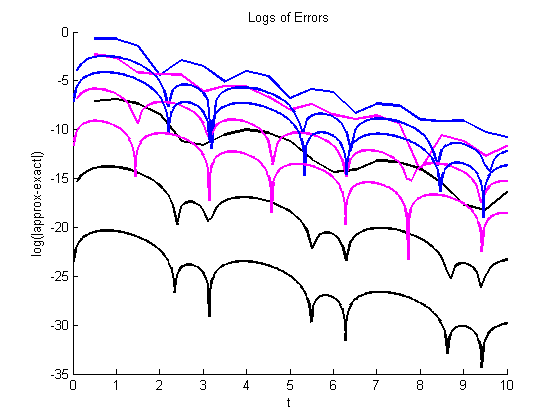
figure(length(Nvalues)+1) % to make sure all of these go in the same figure hold on title('Logs of Errors') xlabel('t'), ylabel('log(|approx-exact|)') % Error for Euler err = log(abs(y1(2:end)-exp(-t1(2:end)).*sin(2*t1(2:end)))); plot(t1(2:end),err,'b','LineWidth',2) maxerr1 = max(abs(y1-exp(-t1).*sin(2*t1))); % Error for RK2 err = log(abs(y2(2:end)-exp(-t2(2:end)).*sin(2*t2(2:end)))); plot(t2(2:end),err,'m','LineWidth',2) maxerr2 = max(abs(y2-exp(-t2).*sin(2*t2))); % Error for RK4 err = log(abs(y3(2:end)-exp(-t3(2:end)).*sin(2*t3(2:end)))); plot(t3(2:end),err,'k','LineWidth',2) maxerr3 = max(abs(y3-exp(-t3).*sin(2*t3))); % Compute approximate rates of convergence if N>Nvalues(1) orderestimateEuler = log(oldmax1/maxerr1)/log(oldh/h) orderestimateRK2 = log(oldmax2/maxerr2)/log(oldh/h) orderestimateRK4 = log(oldmax3/maxerr3)/log(oldh/h) end oldmax1 = maxerr1; oldmax2 = maxerr2; oldmax3 = maxerr3; oldh = h; if N<Nvalues(end) pause end
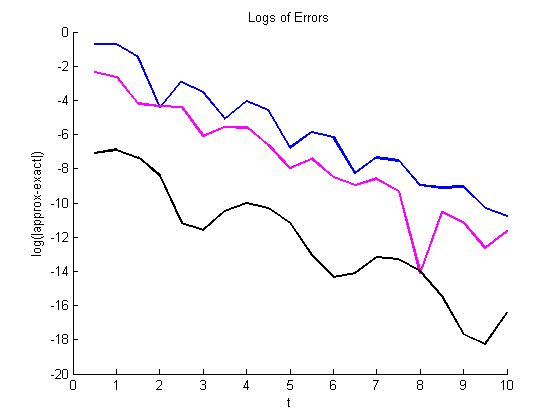
orderestimateEuler =
1.0985
orderestimateRK2 =
2.1706
orderestimateRK4 =
4.2858

orderestimateEuler =
1.0248
orderestimateRK2 =
2.0328
orderestimateRK4 =
4.0640
end